Geography
Job options
Jobs directly related to geography:
- Cartographer
- Commercial/residential surveyor
- Environmental consultant
- Geographical information systems officer
- Planning and development surveyor
- Secondary school teacher
- Town planner
Want to know more about the career options available when taking on a Geography qualification? Why don’t you click the button below to read more and gain support from our aspiration team?
Geography Curriculum Statement
“Shaping the A.C.E Geographers of tomorrow.”
The Geography Department at Haven High strive to achieve this by teaching through a curriculum which promotes…
Accessibility
Compassion
Exploration
INTENT
The purpose of Geography at Haven is to support our learners to become A.C.E. geographers.
(Access, Compassion, Explore)
- We want our learners to access the World around them and broaden their horizons.
- We want our learners to demonstrate compassion for the world, its problems, it’s cultures and it’s peoples.
- We want our learners to be encouraged to explore the World and geographical theories independently, forming their own opinions and views.
Access:
Students should be, regardless of ability, accessing the same curriculum content and exposed to the same geographical terminology.
Students should regularly be exposed to a range of unique, interesting, and wonderous world locations though imagery and case studies.
Students should have access to their own world using appropriate fieldwork techniques and skills, building an understanding of how to learn more about the World using research techniques, independent of the teacher.
Compassion:
Students should have professional, empathetic, and respectful attitudes modelled towards the World by adults around them.
Students should be exposed to the difficult and challenging problems and geographical content to allow them to piece together how it functions.
Students should always be given hope, and balance about the World, it’s people and for the future.
Explore:
Students should be encouraged to choose their own path in life and given opportunities to explore the World around them independently.
Students should be encouraged to enquire and investigate geographical ideas and concepts.
Students should be given the opportunity to interact with the real world, through fieldwork opportunities.
Students should be allowed to make up their own minds about the World, and its challenges.
IMPLEMENTATION OF EDUCATION IN GEOGRAPHY
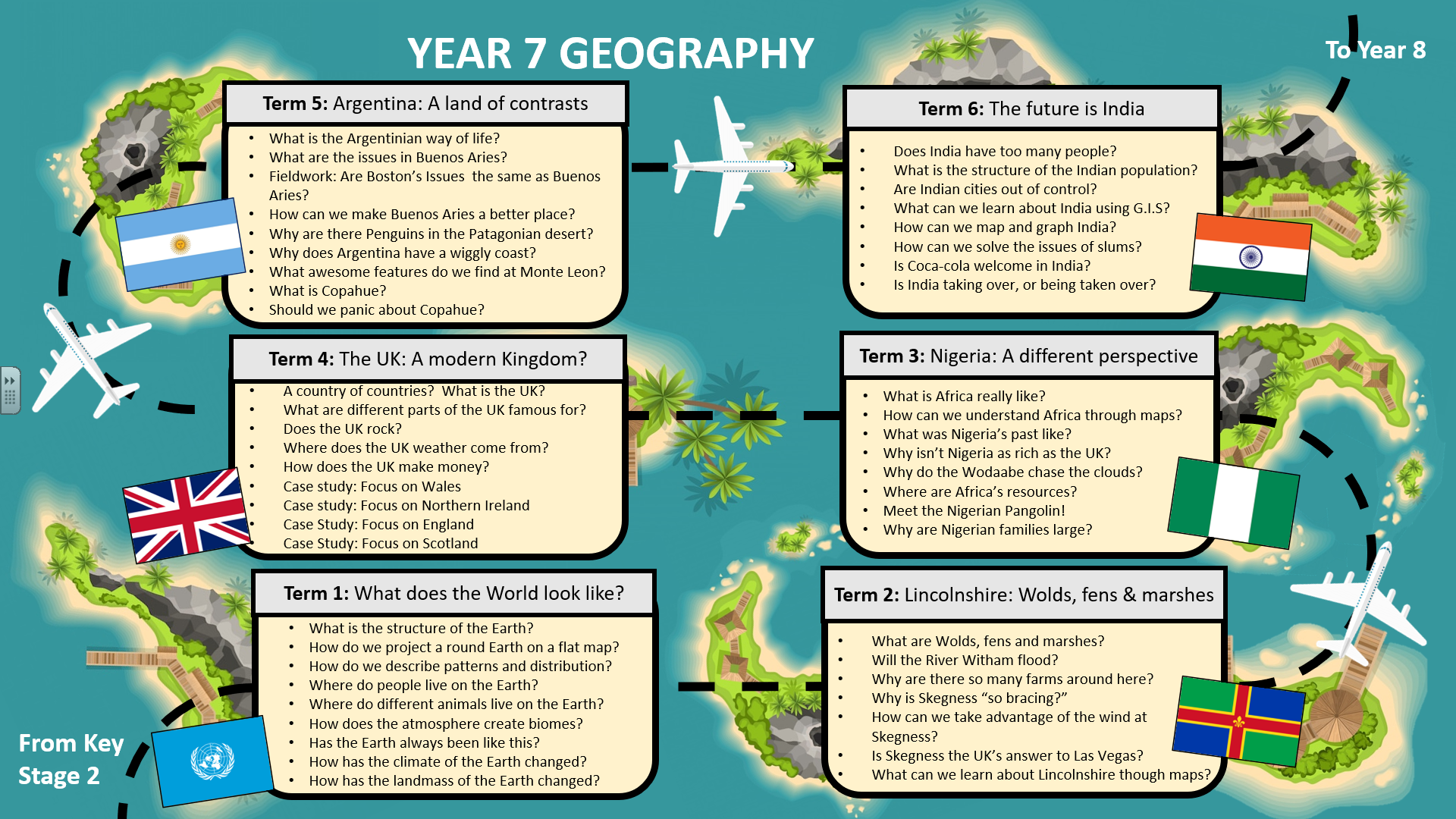
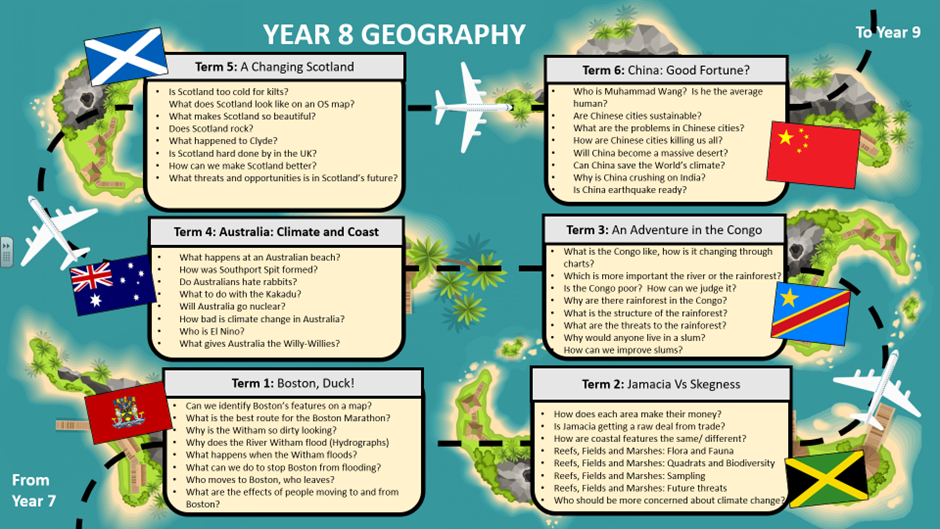
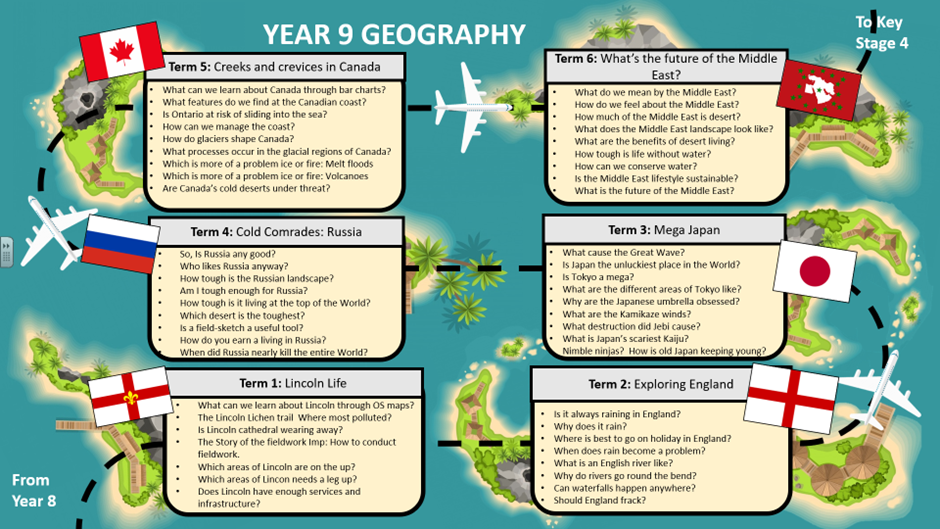
Key Stage 3
Students will access and explore their world thorough place specific modules in which a range of topics are taught. A variety of different and diverse countries (socially, naturally, politically, economically and locationally) will be used as exemplars (including those required under the best practice illustrated by the National Curriculum).
Each module will include content covering 8 main themes: UK landscapes, UK way of life, UK Environment, Global landscapes, Way of the World, World Hazards, Geographical skills and Being a Proper Geographer. This content has been designed to prepare them for GCSE geography, future careers, and full participation in the UK society as global citizen.
As well as modules at an international scale, students will explore a nation of the United Kingdom every year in Key Stage 3 to develop their understanding at a national scale, and also explore local scale module each year. This will provide opportunities for fieldwork at local scale, which is relevant, accessible, and engaging.
The modules will continually cycle content to ensure that the main themes and topics of geography such as (e.g. coastal landscapes, hazards, sustainability) are taught, retaught, built upon as a child develops and visits and revisit’s themes in a range of contexts and countries.
Students will have the opportunity to develop fieldwork skills and research skills at least once per module, through independent investigation lessons and fieldwork lessons. This will enable students to apply what they a have learnt to a real world, context.
Each module will explore a relevant segment of the World map and series of locations to build students understanding of the World map and increase their basic map recognition skills.
Terminology for the GCSE specification will be used throughout Key stage 3 and departmental agreed definitions will be standardized to ensure that students are given the same experience regardless of teaching staff.
To support learning, and geographic development of skills, students will be exposed to standardised skills and methods such as T.E.A graph analysis, P.D.S.E paragraph structure and P.E.L.I.C.A.N distribution to ensure smooth transition of learners through key stages, courses and teacher handovers.
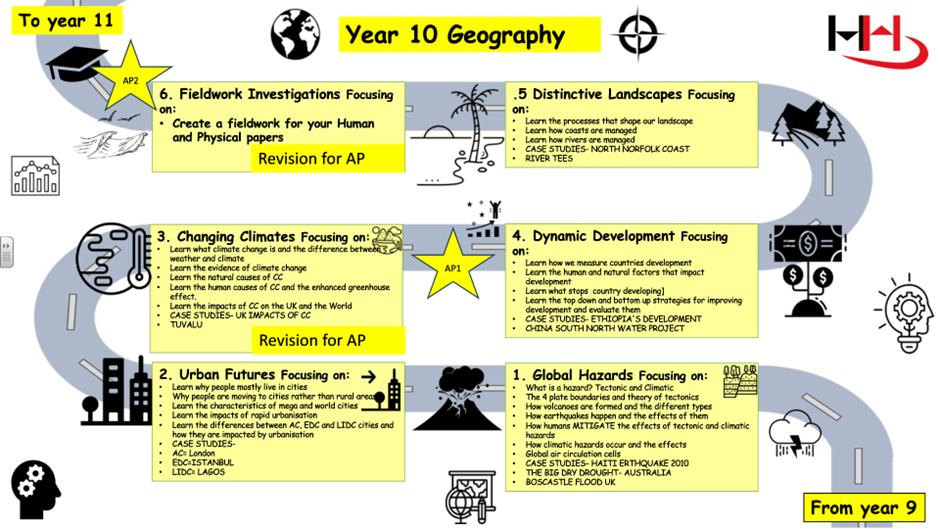
KS4
We follow the OCR B: Geography for Enquiring Minds specification. This is a single tier entry and the option to take geography is open to everyone. It has proved popular in the last few years with us doubling the number of students taking geography into KS4.
From September 2024 Year 10 cohorts will be undertaking the OCR A specification, which is a more thematic approach to Geography to complement our key Stage 3.
Regardless of specification, all G.C.S.E students will be expected to undertake G.C.S.E fieldwork in two varying locations, explore physical and human topical issues and contents in Geography. Both specifications teach Geography through a range of examples from the United Kingdom and the wider world.
Within our G.C.S.E geographical skills are discrete style to ensure that all students are equipped for synoptic and fieldwork elements of the course. 10% of the Geography GCSE incorporate elements of numeracy and mathematics, such as graph analysis, data manipulation and simple calculations.
IMPACT
At the end of a child’s journey studying Geography with us, our students should have developed:
- -An understanding of a variety of social, natural and political landscapes of the world, regardless of their starting cultural capital and world experiences.
- -A good recognition of the World map, its areas, countries, biomes, patterns, similarities and differences.
- -Secure, incremental knowledge of the key themes on geography which will have been regularly revisited in a range of contexts and countries.
- - Skills to explore the World independently and form their own opinions.
- - Knowledge, understanding and skills which enable a child to access a modern UK career in a related geographical field, or be able to continue their learning in another local academic provider.
- -A developing empathy for the World and its problems.
- - An ability to critically analyze information and narratives.
- - Hope, for a better future, for themselves, Boston, the UK and World as a whole.
Cross-curricular links and careers
Geography lends itself naturally to many cross-overs with science and maths. Much of our physical geography is also studied in biology and physics. In addition, through all key stages we will underpin some key mathematical skills, particularly graphical information and statistics. Below is a list of topics and skills that have cross-curricular links:
- Animal adaptation
- Orbit (Milankovitch cycle)
- Hydrological cycle
- Types of erosion and weathering
- Habitats and ecosystems
- Line graphs, bar charts, pie charts, radar charts, rose charts
- Percentages, averages: mean, range, mode
- Height, scale, area and co-ordinates
High level geography students are highly employable. Throughout the two key stages, we make reference to a number of different types of employment. There is explicit reference to the following:
- Cartographer
- Urban planner
- Military
- Politics/Civil Service/Government
- Marine Biologists
- Ecologists
- Primary Industries – Agriculture, mining
- Secondary industries – manufacturing
- Tertiary – Various types of service including retail, education and healthcare
- Quaternary – Scientific research, space engineering, biomedical science
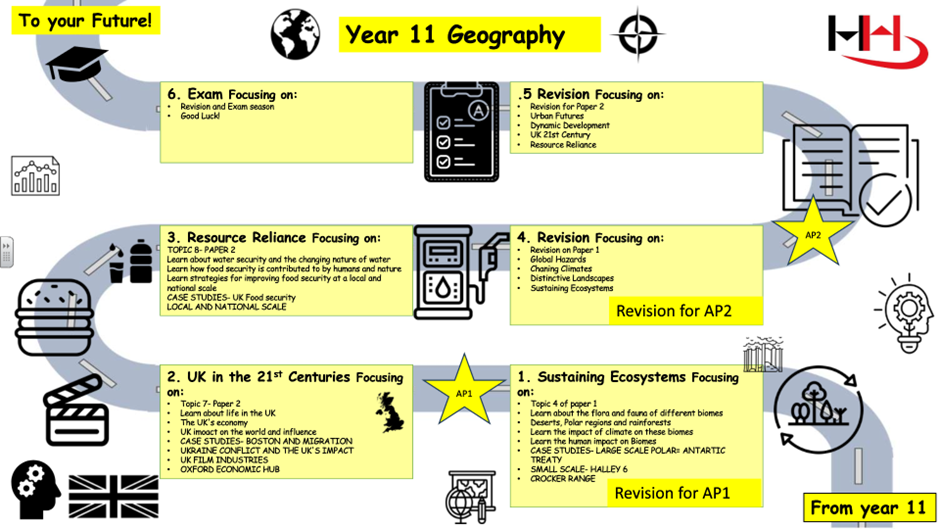
SUBJECT ROADMAPS